Introduction
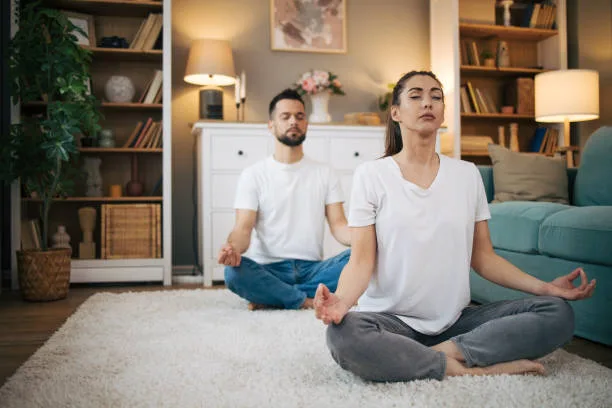
Stress is an inevitable part of life, but its effects on our physical and mental well-being can be mitigated through various strategies. One of the most effective and accessible methods is exercise. From jogging in the park to practicing yoga at home, physical activity has been proven to reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the mechanisms through which exercise works its therapeutic magic, exploring the physiological and psychological aspects of stress reduction.
Endorphin Release: The Feel-Good Hormones
When we engage in physical activity, our bodies release endorphins, neurotransmitters that act as natural painkillers and mood elevators. Endorphins interact with receptors in our brains to reduce the perception of pain and induce feelings of pleasure and euphoria.
Regular exercise boosts endorphin production, leading to a more positive mood and reduced stress levels over time.
Reduction of Cortisol Levels: The Stress Hormone
Cortisol is often referred to as the “stress hormone” because its levels increase in response to stressors. Prolonged elevation of cortisol can contribute to anxiety, depression, and other negative health outcomes. Exercise helps regulate cortisol levels by using up excess energy and promoting relaxation. In males, stress can cause erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence. Take Black Viagra 200mg or Cheap Levitra Online to cure ED.
By lowering cortisol levels, exercise helps the body manage stress more effectively and reduces the risk of stress-related health issues.
Improved Sleep Quality: Restoring Balance
Chronic stress can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and fatigue. Exercise plays a crucial role in improving sleep quality by promoting deeper and more restorative sleep cycles. Physical activity also helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, leading to more consistent sleep-wake cycles.
Quality sleep is essential for stress reduction, and exercise contributes to better sleep patterns, creating a positive cycle of well-being.
Enhanced Brain Function: Sharpening Focus
Regular exercise has been linked to improved cognitive function, including enhanced memory, concentration, and problem-solving skills. Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients that support optimal brain function. Exercise also stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that promotes the growth of new neurons and neural connections.
By boosting brain function, exercise helps individuals better cope with stressors and maintain mental clarity during challenging situations.
Social Interaction and Support: Building Connections
Many forms of exercise, such as group fitness classes or team sports, involve social interaction and support. Engaging with others in a positive and supportive environment can reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common contributors to stress and anxiety.
Social connections fostered through exercise provide emotional support, encouragement, and a sense of belonging, all of which contribute to stress reduction and overall well-being.
Mind-Body Connection: Finding Balance
Practices like yoga, tai chi, and qigong emphasize the connection between mind and body, promoting relaxation, mindfulness, and stress relief. These mind-body exercises combine physical movement with focused breathing and meditation techniques to calm the mind, reduce muscle tension, and enhance overall relaxation.
Mind-body exercises teach individuals how to manage stress through conscious awareness, breathing techniques, and mindfulness practices, fostering a deeper sense of balance and resilience.
Distraction and Outlet for Emotions: Channeling Energy
Engaging in physical activity provides a healthy outlet for pent-up emotions and energy. Exercise serves as a distraction from stressors, allowing individuals to focus their energy and attention on the present moment. Whether it’s hitting the gym, going for a run, or dancing to music, physical activity can help release tension and promote a sense of release.
Exercise offers a constructive way to channel emotions, reduce rumination, and shift focus away from stress triggers, leading to improved emotional well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exercise offers a multifaceted approach to stress reduction, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of well-being. From biochemical changes such as endorphin release and cortisol regulation to cognitive enhancements and social connections, the benefits of regular physical activity extend far beyond physical fitness. By incorporating exercise into our daily routines, we empower ourselves to manage stress more effectively, cultivate resilience, and lead healthier, more balanced lives.